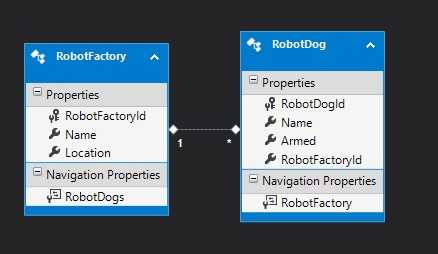
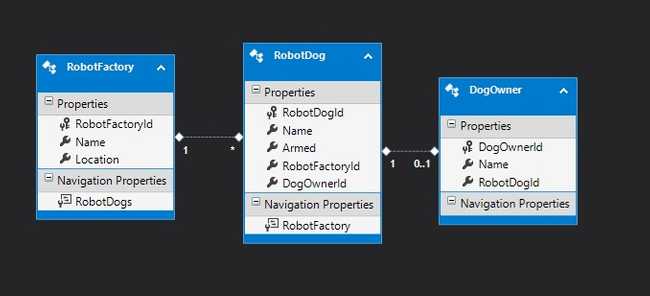
First things first: you should make good use of the navigation properties whenever possible.
The Join Query tool could be your friend if you don’t have any navigation properties but you still need to join two tables (or more).
Starting Point
In this tutorial we will use the simple database created in the Entity Framework Database First Approach, but without using the navigation properties.
Syntax
The first thing you have to know is the syntax:
SELECT [column/columns]
FROM [table1-name]
JOIN [table2-name]
ON [table1-column] = [table2-column]
Join Query
Suppose we want to join the RobotDog and RobotFactory tables, to find the robot dogs produced in the Texan military base.
The Equals keyword is our ally in this mission.
We join the two tables on the RobotFactoryId, taking only the beasts whom factory is in Texas.
{
var robotDogs = (from d in context.RobotDogs
join f in context.RobotFactories
on d.RobotFactoryId equals f.RobotFactoryId
where f.Location == "Texas"
select d).ToList();
}
Or we can use the Join method
.Join(
context.RobotFactories.Where(x => x.Location == "Texas"),
d => d.RobotFactoryId,
f => f.RobotFactoryId,
(d, f) => d)
.ToList();
Select columns to show
You can also choose which column to show after the join. Consider the previous code:
join f in context.RobotFactories
on d.RobotFactoryId equals f.RobotFactoryId
where f.Location == "Texas"
select d).ToList();
You can change that select d in:
Multiple Tables
Not much changes if we want to join multiple tables.
Consider a database with three tables:
We want to find all the people that has dogs from the Texan factory:
join d in context.RobotDogs
on d.DogOwnerId equals o.DogOwnerId
join f in context.RobotFactories
on f.RobotFactoryId equals d.RobotFactoryId
where f.Location == "Texas"
select o).ToList();